High estrogen is clearly anti-health
Some studies on the stress + cyst effects of high estrogen (along with anti-fertility/pregnancy, slow hair regrowth, & tumor promoting effects etc)
But on the other side crashed estrogen isnt great either.
this study showed low vit D could be 1 reason for low estrogen problems,
knocking out vitamin D crashed estrogen/aromatase , and restoring estrogen restored impaired testicle function
 academic.oup.com
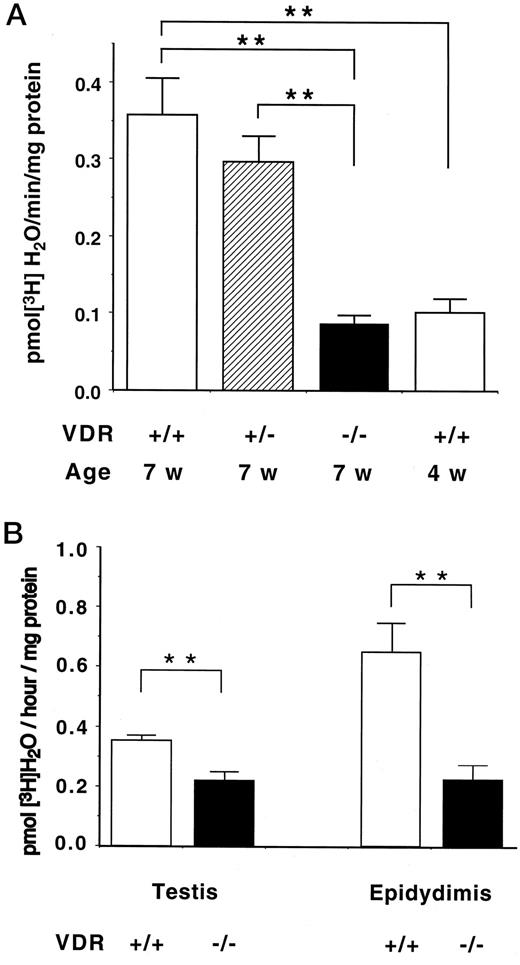
lower aromatase -58.5% in testis of vitamin d knockout group
academic.oup.com
lower aromatase -58.5% in testis of vitamin d knockout group
female mice estrogen levels crashed big time. male estrogen levels - 35%
vitamin d knockout = CYP19 gene which creates aromatase basically doesnt functionally exist. calcium helps bring it back somewhat
restoring vit d restored estrogen levels to normal
might be thinking low testosterone was responsible for the poor testicle function but when they restored just estrogen it restored their testicle measures
(would only testosterone have worked? or is this showing a need for estrogen even in males for testicle function)
* in humans , 1000mg calcium + 1800iu vit D if<30ng/ml , prevents the bone loss from aromatase inhibitors
(supplemental vs food calcium alone doesnt do much for bone loss, was the vit d mainly probably because it helped counter the aromatase inhibition lowering estrogen too much) Vitamin D threshold to prevent aromatase inhibitor-related bone loss
Vitamin D is also 1 key factor in healing chronic wounds.
and estrogen receptor B activation is needed for lung repair, so maybe good for conditions with breathing issues like COPD & emphysema chronically not healing (where there's too little lung copper seen to play a role). Women tend to get less severe covid lung issues than men.
(Though again avoiding extremes either side is key here too - as tipping over to high end looks to worsen asthma incidence after women start postmenopausal estrogen when they're already typically in estrogen dominant state without adding more - does fixing low levels stimulate repair so potentially key, where high levels instead creates further inflammation?)
so if it was high i'd definitely want to be countering it with things like progesterone, high gamma vitamin e, gspe, to lower excessive stress & undesired growths etc
but on the other side i wouldn't want to over-inhibit estrogen unless actively dealing with a tumor. and would try to get it up in certain conditions even (typically not menopause though where estrogen tends to be dominant over progesterone)
Some studies on the stress + cyst effects of high estrogen (along with anti-fertility/pregnancy, slow hair regrowth, & tumor promoting effects etc)
But on the other side crashed estrogen isnt great either.
this study showed low vit D could be 1 reason for low estrogen problems,
knocking out vitamin D crashed estrogen/aromatase , and restoring estrogen restored impaired testicle function

Vitamin D Is an Important Factor in Estrogen Biosynthesis of Both Female and Male Gonads*
Abstract. In the present study, the role of vitamin D in the regulation of estrogen synthesis in gonads was investigated. Vitamin D receptor null mutant mi
female mice estrogen levels crashed big time. male estrogen levels - 35%
vitamin d knockout = CYP19 gene which creates aromatase basically doesnt functionally exist. calcium helps bring it back somewhat
restoring vit d restored estrogen levels to normal
might be thinking low testosterone was responsible for the poor testicle function but when they restored just estrogen it restored their testicle measures
(would only testosterone have worked? or is this showing a need for estrogen even in males for testicle function)
** After estrogen supplementation of VDR null mutant male mice, the histology of the testes revealed no apparent abnormality of the lumen of the seminiferous tubules or epithelial cells at 10 weeks of age, as shown in Fig. 4D. The sperm count and motility in the estrogen-treated mice (n = 3) were increased to the same level in the heterozygous mice.
The sperm count and motility in the estrogen-treated mice (n = 3) were increased to the same level in the heterozygous mice [count, 47.7 ± 5.0 × 106/ml vs. 26.3 ± 7.3 × 106/ml in VDR−/− without treatment
It was recently reported that the P450arom activity of human choriocarcinoma cell lines was stimulated by 1,25-(OH)2D3 and that the VDR response element was identified in the CYP19 gene (30). This would suggest that vitamin D regulates the CYP19 gene directly. Using VDR null mutant mice, not vitamin D-deficient mice, we demonstrated that vitamin D acted to regulate estrogen biosynthesis: this regulation could not be explained by the calcitropic activities alone. These results indicated that vitamin D plays a role in estrogen biosynthesis partially by maintaining extracellular calcium homeostasis. However, direct regulation of the expression of the aromatase gene was also considered.
* in humans , 1000mg calcium + 1800iu vit D if<30ng/ml , prevents the bone loss from aromatase inhibitors
(supplemental vs food calcium alone doesnt do much for bone loss, was the vit d mainly probably because it helped counter the aromatase inhibition lowering estrogen too much) Vitamin D threshold to prevent aromatase inhibitor-related bone loss
Vitamin D is also 1 key factor in healing chronic wounds.
estrogen enhances small intestine repair
Improved Healing of Diabetic Foot Ulcers After High-dose Vitamin D: A Randomized Double-blinded Clinical Trial - PubMed
<span><i>Background</i>. Chronic foot ulcers are a major cause of morbidity in people with diabetes with a lifetime risk of 25%. Treatment is challenging and the recurrence rates of foot ulcers are >50% after 3 years. Vitamin D deficiency is more common in people with diabetes with chronic foot...pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
The intention-to-treat analysis showed a significantly higher rate of ulcer healing in the high-dose group with 21 of 30 (70%) healed ulcers compared to 12 of 34 (35%) in the low-dose group (P = .012). Median ulcer reduction at final follow-up was 100% (interquartile range [IQR]: 72-100) in the high-dose group and 57% (IQR: -28 to 100) in the low-dose group
estrogen can also be useful for increasing iron & copper uptake in deficiency , which are both core needs for mitochondria functionEstrogen enhances female small intestine epithelial organoid regeneration
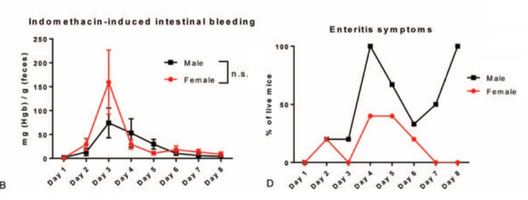
Using a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced intestinal damage mouse model, we verified that female mice recover faster than males following acute intestinal insult.
Using ex vivo intestinal organoid cultures, we showed that estrogen is necessary and sufficient in enhancing the female organoid formation from breached isolated crypts via the estrogen receptor β receptor. Thus, estrogen promotes female intestinal epithelial organoid regeneration to lower the incidence of intestinal bleeding and ulceration
<-- initially more bleeding but rapid difference in amount of mice with symptoms, and body weight return (food intake)
both male and female C57BL/6J mice showed intestinal epithelial damage (Fig. 2A), bleeding (Fig. 2B), and body weight loss (Fig. 2C). However, female mice recovered from the intestinal damage substantially faster than male mice, reflected by the increase rate of recovery from weight loss (Fig. 2C) and faster elimination of enteritis symptoms (Fig. 2D). This indicates that female mice are more robust in intestinal epithelial regeneration after damage.
The addition of a physiologically relevant concentration of β-estradiol in estrogen-free LWRN cultures significantly increased the number of organoids formed from female crypts (Fig. 4E). These data suggest that estrogen is necessary and sufficient for the enhanced robustness of the regeneration of female intestinal epithelium. However, the factor that β-estradiol could not fully restore female organoid growth when grown in hormone-depleted medium suggests that other hormone or lipophilic factors (high affinity to activated charcoal) are required for the maximal robustness of female intestinal epithelial regeneration.
Female mouse intestinal epithelium (isolated and cultured as organoids) expresses detectable levels of ERβ and G protein-coupled estrogen receptor, but does not express ERα
(Does male human intestinal epithelium express ERb?) Linking estrogen receptor β expression with inflammatory bowel disease activity <--- higher ERb in responsive CD/UC patients, Estrogen receptor-β (ERβ) is the most abundant estrogen receptor in the colon
and estrogen receptor B activation is needed for lung repair, so maybe good for conditions with breathing issues like COPD & emphysema chronically not healing (where there's too little lung copper seen to play a role). Women tend to get less severe covid lung issues than men.
(Though again avoiding extremes either side is key here too - as tipping over to high end looks to worsen asthma incidence after women start postmenopausal estrogen when they're already typically in estrogen dominant state without adding more - does fixing low levels stimulate repair so potentially key, where high levels instead creates further inflammation?)
Estrogen regulates pulmonary alveolar formation, loss, and regeneration in mice
Estrogen replacement, after alveolar loss, induces alveolar regeneration, reversing the architectural effects of ovariectomy. These studies 1) reveal estrogen receptors regulate alveolar size and number in a nonredundant manner, 2) show estrogen is required for maintenance of already formed alveoli and induces alveolar regeneration after their loss in adult ovariectomized mice, and 3) offer the possibility estrogen can slow alveolar loss and induce alveolar regeneration in women with COPD. @iLoveSugar @PeterSN
so if it was high i'd definitely want to be countering it with things like progesterone, high gamma vitamin e, gspe, to lower excessive stress & undesired growths etc
but on the other side i wouldn't want to over-inhibit estrogen unless actively dealing with a tumor. and would try to get it up in certain conditions even (typically not menopause though where estrogen tends to be dominant over progesterone)
Attachments
Last edited: