Chlorophyllin is a derivative of chlorophyll, aka water soluble chlorophyll
Increases White blood count, Red blood count, Hemoglobin slightly, by 14 and 28 days , (from normal baselines, in rats with oxidative stress induced lowering of these i bet would be big effect)
https://www.cureus.com/articles/138...rent-injection-doses-of-liquid-chlorophyll#!/
There's about 4mg copper in 100mg chlorophyllin. (some supplement forms have magnesium instead of copper).
Think it's copper II which usually found as supplements that arent absorbed well. But iron chlorophyllin is as effective as heme iron for intestinal absorption , because the chlorophyllin helps intestinal transport (similar structure to hemoglobin).
I think the same thing happens with copper Analysis of the therapeutic effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin tablet in treating 60 cases of leukopenia - PubMed
low copper induces leukopenia , low neutrophils (but the neutrophils get deformed and pass through endothelial wall easier, which can play a role in many disorders)
sodium copper chlorophyllin fixes the leukopenia in humans
which makes me think the chlorophyllin is helping the copper absorb well
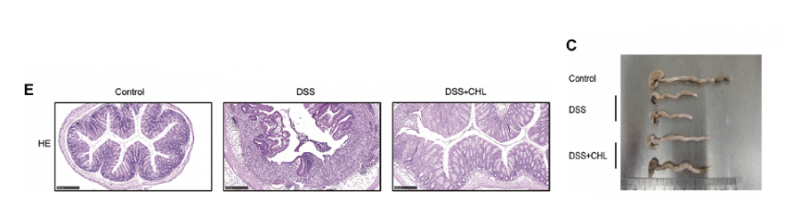
Helps heal colitis when given after colitis induction
https://www.researchgate.net/public...D_by_suppressing_autophagy_activation_in_mice
(i think dose = ~40mg human). visually looks like 50% healing

used topically way back for wound / ulcer healing


Its is a potent oxidative stress protector. scavenges free radicals directly, increases protective enzymes
maybe even more potent than glutathione for protecting mitochondria. protects DNA.
The Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Chlorophylls and Pheophytins
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11018464/
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/cpb1958/32/2/32_2_716/_article
Protects DNA in bone marrow at low dose <10mg orally
(but maybe needed higher dose to protect against the other compound?)
https://www.eurekaselect.com/article/112815
It's similar in structure to hemoglobin so also binds iron (iron chlorophyllin is as effective as heme iron for intestinal absorption) , and might be another mechanism behind its anti-carcinogen properties by oxidizing them, so could have dual properties (i guess re-releases the iron as its shown to help raise red blood counts?)
DNA protective against radiation and other oxidative stressors
250mg lowest dose tested was just as effective as more which implies no further benefit from 250mg. (effect should work at lower amounts too)
nice effect on small intestine in liver fibrosis / cirrhosis
https://www.frontiersin.org/files/A...09-01671-HTML/image_m/fphys-09-01671-g004.jpg
inhibits kidney stone growth / oxalates Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin on the formation of calcium oxalate crystals in rat kidney - PubMed
Increases White blood count, Red blood count, Hemoglobin slightly, by 14 and 28 days , (from normal baselines, in rats with oxidative stress induced lowering of these i bet would be big effect)
https://www.cureus.com/articles/138...rent-injection-doses-of-liquid-chlorophyll#!/
There's about 4mg copper in 100mg chlorophyllin. (some supplement forms have magnesium instead of copper).
Think it's copper II which usually found as supplements that arent absorbed well. But iron chlorophyllin is as effective as heme iron for intestinal absorption , because the chlorophyllin helps intestinal transport (similar structure to hemoglobin).
I think the same thing happens with copper Analysis of the therapeutic effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin tablet in treating 60 cases of leukopenia - PubMed
low copper induces leukopenia , low neutrophils (but the neutrophils get deformed and pass through endothelial wall easier, which can play a role in many disorders)
sodium copper chlorophyllin fixes the leukopenia in humans
which makes me think the chlorophyllin is helping the copper absorb well
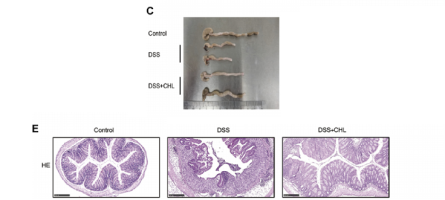
Helps heal colitis when given after colitis induction
https://www.researchgate.net/public...D_by_suppressing_autophagy_activation_in_mice
(i think dose = ~40mg human). visually looks like 50% healing
We further determined if the administration of CHL can relieve established colitis in mice. chlorophyllin was added to drinking water at 40 mg/L.
Strikingly, the DSS-induced mortality at 62.5% rate in mice at day 15 was substantially reduced by chlorophyllin treatment, showing a reduced mortality rate at 12.5%, which agreed with relieving symptoms of colitis
used topically way back for wound / ulcer healing
Its is a potent oxidative stress protector. scavenges free radicals directly, increases protective enzymes
maybe even more potent than glutathione for protecting mitochondria. protects DNA.
The Antioxidant and Free Radical Scavenging Activities of Chlorophylls and Pheophytins
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11018464/
our results show that CHL is highly effective in protecting mitochondria, even at a low concentration of 10 microM. The antioxidant ability, at equimolar concentration, was more than that observed with ascorbic acid, glutathione, mannitol and tert-butanol. When CHL was fed to mice at a dose of 1% in drinking water, there was a significant reduction in the potential for oxidative damage in cell suspensions from liver, brain and testis.
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/cpb1958/32/2/32_2_716/_article
When sodium copper chlorophyllin (Cu-Chl-Na) was given intraperitoneally to rats (two doses of 50 or 100mg/kg at 18 and 2h prior to sacrifice), the soluble fraction of liver in injected animals showed an inhibition of the ascorbic acid- and NADPH-stimulated lipid peroxidation in hepatic microsomes from untreated rats.
These findings suggest that the administered Cu-Chl-Na or substance (s) derived from Cu-Chl-Na is taken into the liver and distributed among the mitochondria, microsomes and soluble fraction in an active form functioning as an antioxidant. Subsequently, a single injection of Cu-Chl-Na was observed to prevent effectively the impairment of hepatic microsomal functions (as indicated by the depression of glucose-6-phosphatase and drug-metabolizing enzyme system) resulting from ascorbic acid-induced lipid peroxidation.
Protects DNA in bone marrow at low dose <10mg orally
(but maybe needed higher dose to protect against the other compound?)
Fahey et al. [37] reported that chlorophyll can improve the function of essential detoxification pathways. Chlorophyllin was 410-fold more potent as a phase 2 enzyme inducer than chlorophyll, since it has other detoxification properties because it is much more water-soluble than chlorophyll. Antioxidant activity of chlorophyll from plant leave also reported by Sakagami et al. [38] showed that Sasa senanensis Rehder leaf extract containing Fe(II)-chlorophyllin demonstrated superoxide anion and hydroxyl radical-scavenging activity five times higher than a similar product containing Cu(II)-chlorophyllin and comparable to a product containing Cu(II)-chlorophyllin
https://www.eurekaselect.com/article/112815
Conclusion: Therefore, the present study reports, for the first time, the screening of phytobased bioactive CHL for preventing/limiting the extent of food-additive-induced genotoxicity and mitochondrial dysfunction and serves as an advanced therapeutic tool in the management of diabetes.
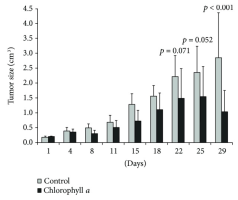
Dual actions of the antioxidant chlorophyllin, a glutathione transferase P1-1 inhibitor, in tumorigenesis and tumor progression - PubMed in vivo treatment with chlorophyllin increased the GSH levels in the liver and significantly decreased DNA damage in the blood, liver, and tumor tissues. Even though tumorigenesis was delayed in rats receiving chlorophyllin before MNU injections, once the tumors emerged, the progression of tumor appeared to be faster than in the animals that received the carcinogen only [what's good for healthy cells can also be good for cancer cells] Chlorophyllin displayed genoprotective effects that initially delayed tumorigenesis. However, once the tumors were established, it may act as a promoter that facilitates tumor growth, potentially by a mechanism independent of cell proliferation and viability. Our results underline the pros and cons of antioxidant treatment in cancer, even if it has a capacity to inhibit GST P1-1.
Chlorophyllin disables potent carcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heterocyclic amines by forming complexes with these chemicals that limit the ability of these toxins to bind to normal cells to inflict malignant changes
It's similar in structure to hemoglobin so also binds iron (iron chlorophyllin is as effective as heme iron for intestinal absorption) , and might be another mechanism behind its anti-carcinogen properties by oxidizing them, so could have dual properties (i guess re-releases the iron as its shown to help raise red blood counts?)
DNA protective against radiation and other oxidative stressors
250mg lowest dose tested was just as effective as more which implies no further benefit from 250mg. (effect should work at lower amounts too)
nice effect on small intestine in liver fibrosis / cirrhosis
https://www.frontiersin.org/files/A...09-01671-HTML/image_m/fphys-09-01671-g004.jpg
In an animal model, dietary supplementation of chlorophyllin at 4 mg/kg body weight inhibited the development of MNNG-induced fore stomach carcinoma.
In this study we found that chlorophyllin is able to ameliorate the hepatic toxin induced liver fibrosis. Mechanistically, chlorophyllin may work on two levels. First, we found that chlorophyllin can directly impact intestinal epithelial cells and suppress inflammatory signals that are initiated by LPS and TNF-alpha.
In particular, administration of chlorophyllin can promptly restore eubiosis, showing restoration of Bacteroidetes and reduction of Firmicutes Such a finding is important because it can also explain the observed reduction of plasma endotoxin, preassembling through the prevention of the death of Bacteroidetes, the Gram-negative bacteria that may contribute to the plasma endotoxin via intestinal-hepatic circulation.
inhibits kidney stone growth / oxalates Effect of sodium copper chlorophyllin on the formation of calcium oxalate crystals in rat kidney - PubMed
Attachments
Last edited: