Ras
Member
- Joined
- Sep 12, 2015
- Messages
- 938
That link to Riddick's book is not working for me. Do you have another source for the book? Google didn't help me much.Hi, I stumbled upon Dr. Ray Peat while preparing a lecture on the discoveries by Dr. Gilbert Ling and Prof. Gerald Pollack on the structured water. I have known Ling's discoveries for quite some times but had no idea what health consequences this had until listening to Peat's YouTube videos!
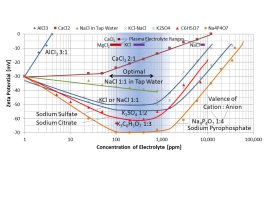
Now there is another very important health secret and it has also to do with water, but not in the cells, where it is structured, but in blood, where it is highly liquid! This has to do with the proper balance of electrolytes and their valence ratios. Thomas M. Riddick wrote about this in his book 'Control of Colloid Stability through Zeta Potential - With a closing chapter on its relationship to cardiovascular disease' and can be found here:
Thomas M. Riddick's Book
His findings on cardiovascular health were applied by Dr. T.C. McDaniel, who celebrated his 100th birthday this May (2014). Dr. McDaniel also wrote a book with the title 'Disease Reprieve', in which he wrote about his experience as a student of medicine and his own trouble with heart arrhythmia, which he was able to get rid of after reading about the Zeta Potential in Riddick's book. Dr. McDaniel sells a supplement 'Zeta Aid' which is an anionic surfactant that stabilizes the blood. He claims that this will get rid of heart disease.
T.C. McDaniel's Website
So it is interesting to note, that there are two completely different types of water in our bodies, the highly structured water in the cells, and the highly optimized liquid, the blood, a suspension stabilized by the Zeta Potential of the dissolved electrolytes.
Only to mention it briefly, aluminum chloride (AlCl[sub]3[/sub], valence ratio 3:1) will weaken the Zeta Potential, while potassium citrate (valence ratio 1:3) will strengthen the Zeta Potential.