OP
LeeLemonoil
Member
- Joined
- Sep 24, 2016
- Messages
- 4,265
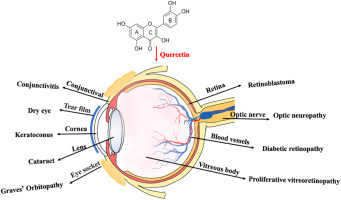
These eyedrops with Vit B2 promote B2 as an active that „absorbs“ or protects against UV and bluelight and is recommended for monitor work. Can’t vouch for the legitimacy of such claims.
 de.farmaciacastellanos.com
de.farmaciacastellanos.com

Augentropfen spezielles UV-Licht
Barriere zum Schutz vor blauem Licht durch Geräte und UV-Strahlung