Repurposing of the antibiotic Doxycycline as an antiviral and anti-cancer therapeutic
A literature review
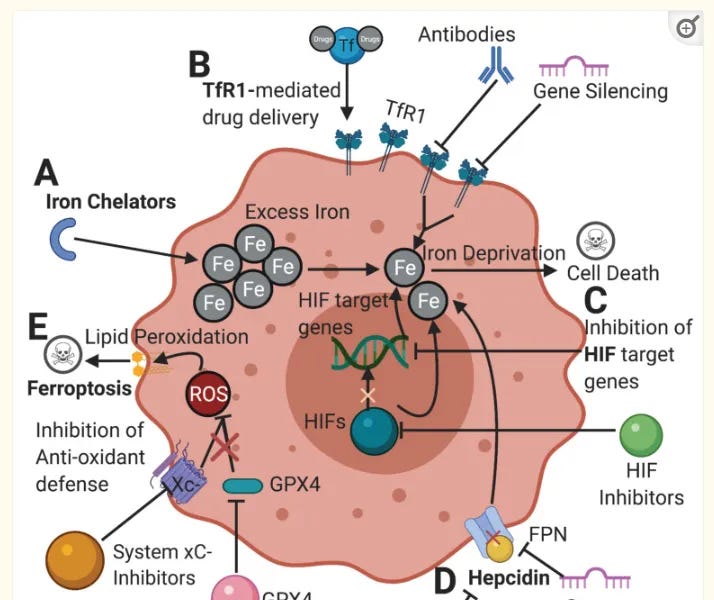
This review begins with a brief introduction to doxycycline as a drug: its uses, side effects, history and chemical formula with the 5-ringed structure typical of the tetracyclines.Doxycycline and its iron chelation mechanisms and effects are then described.
In 2021, Faure et al performed in vitro experiments to investigate the synergistic interactions between five tetracyclines and tobramycin with an iron chelator (CP762) against two reference strains and nine clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients.
They found that as it binds with high affinity to iron this inhibited its antibacterial effects by competing with the magnesium binding site on the bacterial ribosome. The addition of another iron chelator, CP762, synergistically restored the magnesium bridge binding.
In 1999 Alkawash et al appeared to find lactoferrin/doxycycline antibacterial synergy, and by a large margin of 32 to 64 fold against B. cepacia.
In 2015, Wu et al investigated its effects in vitro on the replication of vesicular stomatitis virus.
Of particular note here for also treating long covid/vaccine sequalae is that doxycycline acts as both an antiviral and an anticancer therapeutic agent by the induction of expression of the key tumor suppressor p53.
In 2020, Mosquera-Sulbaran and Hernández-Fonseca published a review on the use of tetracycline as an anti COVID-19 therapeutic.
2 clinical trials using doxycycline and ivermectin are then discussed. No results were available from the first of these, but from the second the only participants to die of COVID-19 were 3 from the placebo group of 200. Duration and severity of symptoms in the treatment group were also significantly reduced.
Three papers investigating iron chelation, inhibition of tumors and metastasis are reviewed. Buss et al (2003) recognized the potential of using iron chelation in cancer therapy and their possible synergistic effects.
From 2013, Richardson et al review how the iron chelator DFO can inhibit key signalling pathways which induce epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) in pancreatic cancer and other tumors. EMT is described.
A paper by Morales and Xue (2021) reviews the targeting of iron metabolism in cancer therapy.
Ubiquitination is described, as is evidence for the HIF inhibitory effects of both lactoferrin and ivermectin. This is important for working synergistically with doxycycline to help avoid resistance from cancer cells.
To complete this review, four papers discuss the anticancer properties of doxycycline.
In 1998, Fife et al found that, in vitro, doxycycline can significantly inhibit the growth of prostate and breast cancer tumors by the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and induction of apoptosis.
From 2016, Zhang et al conducted an in vitro study using human breast cancer cell lines.
A paper by Zhu et al (2017) conducted an in vitro investigation into how doxycycline synergizes with the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin to inhibit the proliferation of castration-resistant prostate cancer cells, a condition that was previously untreatable.
And from 2019, Markowska et al conducted a review into the repositioning of doxycycline, salinomycin, monensin and ivermectin as cancer drugs.
To conclude this Substack, dosing and contraindications for doxycycline monohydrate are considered.
