bistecca
Member
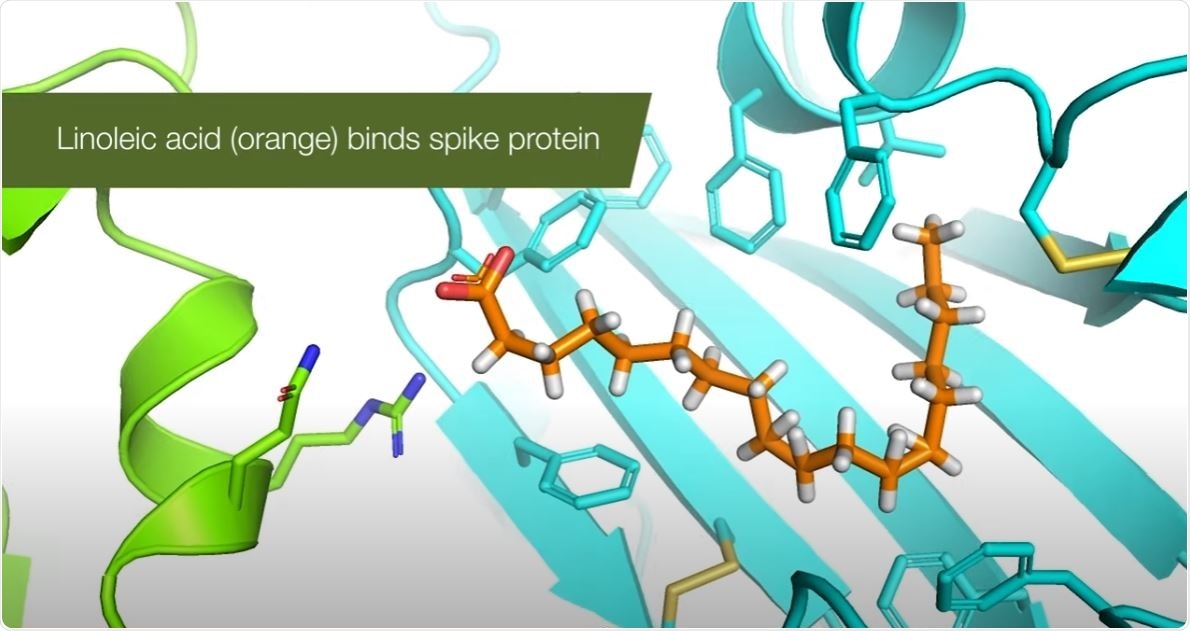
>Upon the analysis of the molecular structure of the spike protein, the team has found something interesting. They revealed the presence of a small molecule, called linoleic acid (LA), which was discovered in a customized pocket within the spike protein.
 www.news-medical.net
www.news-medical.net
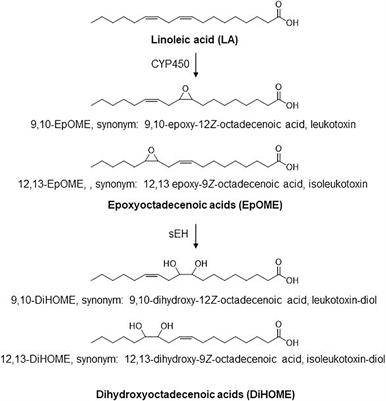
>It is clear that the two regioisomeric linoleic acid diols (DiHOMES) had highly elevated concentrations in these COVID-19 positive patients, as did their precursor epoxides (EpOMEs; Table 2).
>The high abundance of linoleate as a substrate, coupled with the increased biosynthesis of anti-inflammatory EpFA during severe coronavirus infections and the induction of sEH in an inflammatory state (Kodani and Hammock, 2015) may explain the increased rate of synthesis and concentration of leukotoxin diols observed in COVID-19 patients in our study. This finding raises the possibility that amelioration of COVID-19 symptoms may be achieved in part by reduction of omega-6-rich diet,
 www.frontiersin.org
www.frontiersin.org
wow who could have seen this coming..

Linoleic acid binds SARS-CoV-2 spike protein
Now, a team of researchers at the Max Planck-Bristol Center for Minimal Biology and Bristol's School of Biochemistry has identified a druggable pocket in the virus's spike protein that can be used to prevent the infection of cells. The study findings, published in the journal Science, are a...
>It is clear that the two regioisomeric linoleic acid diols (DiHOMES) had highly elevated concentrations in these COVID-19 positive patients, as did their precursor epoxides (EpOMEs; Table 2).
>The high abundance of linoleate as a substrate, coupled with the increased biosynthesis of anti-inflammatory EpFA during severe coronavirus infections and the induction of sEH in an inflammatory state (Kodani and Hammock, 2015) may explain the increased rate of synthesis and concentration of leukotoxin diols observed in COVID-19 patients in our study. This finding raises the possibility that amelioration of COVID-19 symptoms may be achieved in part by reduction of omega-6-rich diet,

Frontiers | Plasma Linoleate Diols Are Potential Biomarkers for Severe COVID-19 Infections
Polyunsaturated fatty acids are metabolized into regulatory lipids important for initiating inflammatory responses in the event of disease or injury and for ...
wow who could have seen this coming..
